Empowering Safety and Speed: How AI is Transforming Oil & Gas Operations with Predictive 4IR Intelligence
The Fourth Industrial Revolution and the New Era of Oil & Gas
The oil and gas sector is experiencing an unprecedented transformation, propelled by the convergence of digital technologies at the heart of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR, or Industry 4.0). This revolution signifies not just another incremental upgrade, but a fundamental reimagining of how energy companies operate, innovate, and remain competitive in an increasingly dynamic market. Innovative technologies—ranging from Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data analytics, supercomputing, and quantum computing, to robotics, IIoT, cloud computing, and blockchain—are intertwining physical assets with digital intelligence. The result is a seismic shift towards smarter, faster, safer, and more cost-efficient operations across the upstream, midstream, and downstream value chain.
The rise of SaaS (Software as a Service) providers—such as Innobles Smart Technology—is empowering even small and mid-sized oil and gas operators to leapfrog legacy limitations and embrace future-proof solutions without the exorbitant investment and risk associated with large-scale, on-premises systems. This blog explores the digital innovations shaping oil and gas, with a focus on tangible use cases—from AI-powered safety and process automation to the deployment of supercomputing and quantum techniques in seismic imaging and reservoir simulation. We reveal how these advancements, championed by agile SaaS innovators, lead to radical work simplification, higher operational resilience, and measurable cost savings.
AI and Big Data Analytics: From Data Silos to Dynamic Insights
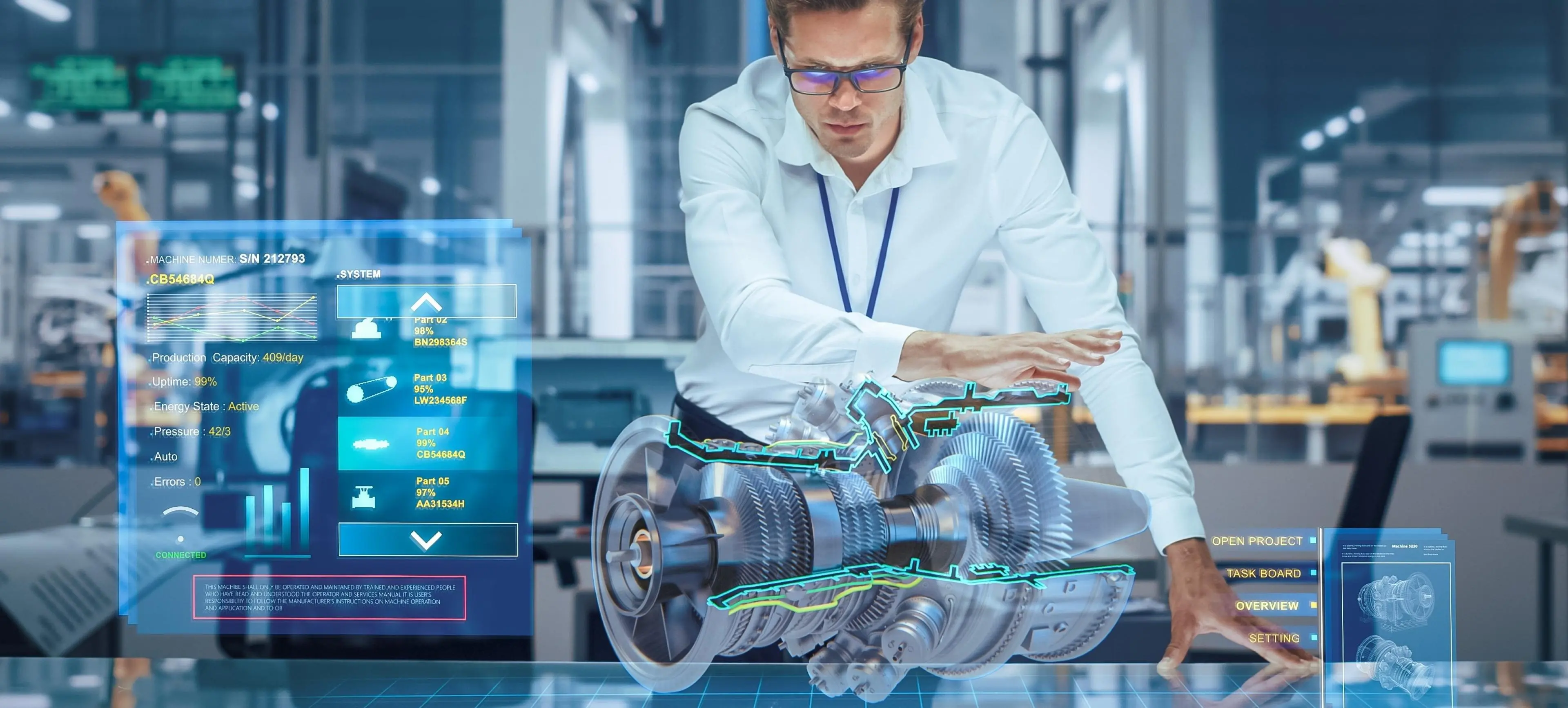
Digital oil fields today are awash in data: seismic readings, equipment telemetry, environmental sensors, production logs, and market variables all flow at high speed. The real challenge is turning this deluge into insight, action, and advantage. AI and Big Data analytics address this by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive forecasting, and automated decision-making. AI-driven platforms ingest, analyze, and synthesize data from structured and unstructured sources—identifying patterns, predicting failures, optimizing production, and even advising on market positioning.
Key Big Data Use Cases in Oil and Gas:
-
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms predict equipment failures, enabling maintenance teams to schedule repairs proactively and avoid costly downtime and catastrophic incidents.
- Seismic Data Analysis: Machine learning swiftly interprets seismic data to identify optimal drilling sites, reducing time-to-oil and failure risk.
- Production Optimization: Data-driven models adjust extraction parameters in real time, improving output while minimizing operational costs.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Advanced analytics optimize logistics, inventory, and procurement, reducing delays and costs across complex supply chains.
- HSE Compliance: AI-powered pattern recognition detects anomalies and near misses in safety-critical systems, generating early warnings and compliance reports.
Benefits of AI and Big Data:
- Operational Efficiency: Automation reduces manual errors and accelerates workflows, leading to substantial time and cost savings.
- Enhanced Safety: Predictive analytics and AI-powered monitoring reduce human exposure in hazardous environments and help prevent incidents before they escalate.
- Faster, Better Decision-Making: Integrated analytics turn scattered, siloed data into actionable intelligence for leaders and field operators alike.
The integration of AI with Big Data is not a theoretical promise; established oil majors such as BP, Shell, and ExxonMobil have documented up to 40% reductions in equipment downtime and substantial operational cost savings after deploying AI-driven predictive maintenance and seismic analytics.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Work Automation
The oil and gas industry is rich in repetitive, rule-based, and data-intensive activities, ranging from invoice processing and compliance documentation to equipment inspection and inventory management. RPA harnesses software bots to take over these routine workflows, freeing skilled personnel to focus on higher value tasks, improving accuracy, and boosting productivity.
Use Cases for RPA:
- Back Office Automation: RPA bots manage financials, HR onboarding, procurement, and invoicing, dramatically reducing cycle times and minimizing errors.
- Field Operations: Automated scheduling of inspections, digital workflow approvals, and procurement requisition management streamline frontline processes.
- Compliance Reporting: RPA enables real-time regulatory submissions and audit trails, reducing regulatory risk and operational bottlenecks.
Impact and Advantages:
- Reduced Process Errors: Automation reduces human error rates by up to 95% in compliance and documentation management.
- Cost Efficiency: Companies report 30–50% savings from automating transactional processes, particularly in shared services and field logistics.
- Scalability: RPA solutions can scale rapidly across regions and processes with minimal marginal cost.
Digital automation forms the foundation for further innovation, providing the standardized, high-quality data needed for advanced analytics and AI modelling.
Also read:
- Innobles Smart Technologies: Your Partner in Agentic Transformation
- Emerging Trends in AI and Government Policies
- Cloud Data Encryption Guide for IT Professionals
- Innobles Smart Technologies: Your Partner in Agentic Transformation
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Real-Time Sensing and Control
IIoT—sensors, smart devices, and digital actuators connected via secure networks—enables remote monitoring, automated diagnostics, and seamless equipment control. In the oil and gas sector, IIoT transforms asset performance management, environmental compliance, and safety assurance.
Oil & Gas IIoT Use Cases:
- Real-Time Asset Monitoring: Sensors track temperature, pressure, corrosion, flow rates, and vibration along pipelines and at the wellhead, triggering alerts before failures occur.
- Emissions and Environmental Control: IIoT devices monitor emissions and discharge parameters, providing data for increased regulatory compliance and environmental stewardship.
- Remote Infrastructure Management: Through IIoT, offshore rigs and distant pipelines can be managed and serviced with fewer site visits.
Strategic Advantages:
– Proactive Maintenance: Early fault detection reduces unplanned outages and extends asset lifespans.
– Cost Reduction: Remote asset management reduces site visits and associated travel and labor costs—critical for geographically distributed assets.
– Safety: Sensors in hazardous areas minimize human exposure and improve emergency response times.
Successful IIoT deployments in oil and gas rely on robust data platforms and interoperability standards, often offered as part of modern SaaS solutions.
Contact us at Reachus@innobles for Free Consulation